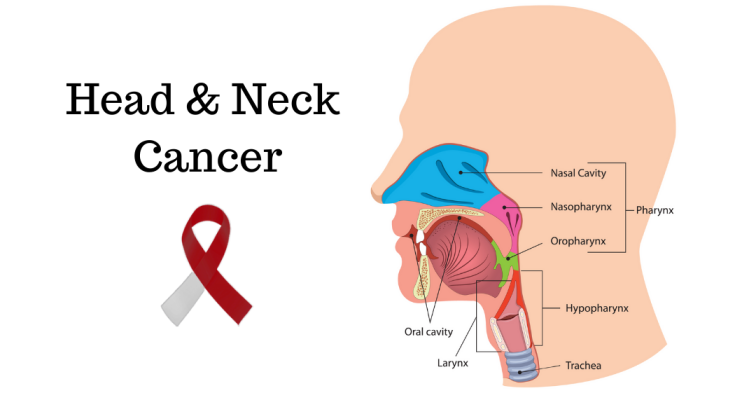
Understanding Head and Neck Cancer
Head and neck cancer refers to a group of cancers that develop in the mouth, throat, voice box (larynx), nose, and sinuses. While not as commonly discussed as lung or breast cancer, head and neck cancers account for nearly 4% of all cancers in the U.S..
Many cases are curable when caught early, but because symptoms can mimic common illnesses, they often go unnoticed. Knowing the signs, risk factors, and when to seek medical attention can be life-saving.
Types of Head and Neck Cancer
Head and neck cancers are classified based on where they develop:
Oral Cancer (Mouth Cancer)
- Forms in the tongue, lips, cheeks, gums, and roof or floor of the mouth.
- Early signs include persistent mouth sores, red or white patches, and difficulty chewing.
Throat Cancer (Pharyngeal Cancer)
- Affects the pharynx (throat), which includes the tonsils and soft palate.
- Symptoms often involve difficulty swallowing and persistent sore throat.
Laryngeal Cancer (Voice Box Cancer)
- Develops in the larynx (voice box), which contains the vocal cords.
- Common in smokers and leads to hoarseness or voice changes.
Nasal and Sinus Cancer
- Starts in the sinuses or nasal cavity and may cause chronic congestion or nosebleeds.
Salivary Gland Cancer
- Occurs in the glands that produce saliva, often leading to a painless lump under the jaw or near the ear.
Each type of head and neck cancer presents differently, but many share similar early warning signs.
Common Symptoms of Head and Neck Cancer
Early symptoms can be subtle and easily mistaken for minor issues. It’s important to be aware of:
- Persistent sore throat or hoarseness that doesn’t improve
- Difficulty swallowing or the sensation of something stuck in the throat
- Unexplained weight loss
- Ear pain or fullness (especially in one ear)
- A lump or swelling in the neck, throat, or jaw
- Chronic nasal congestion or frequent nosebleeds
- Numbness or tingling in the face or mouth
- Changes in voice or difficulty speaking
If these symptoms last more than two weeks, it’s essential to seek an evaluation from an ENT specialist for early detection.
How Is Head and Neck Cancer Diagnosed?
Early detection greatly improves the chance of successful treatment. If symptoms persist, an ENT specialist may recommend:
Physical Examination
- Checking for lumps in the neck or abnormal growths in the mouth or throat.
Endoscopy (Laryngoscopy or Nasopharyngoscopy)
- A small camera is inserted through the nose or mouth to examine the throat, voice box, or sinuses.
Imaging Tests (CT Scan, MRI, or PET Scan)
- Helps detect tumors and determine their size and spread.
Biopsy
- If an abnormal tissue is found, a small sample is taken for lab analysis to confirm cancer.
HPV Testing
- For throat cancers, HPV testing may be conducted to determine the best treatment approach.
Treatment Options for Head and Neck Cancer
Treatment depends on the type, location, and stage of cancer, but common options include:
Surgery
- Removes the tumor and, in some cases, affected lymph nodes.
- Neck surgeries may be necessary for larger cancers.
Radiation Therapy
- Uses high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells.
- Often used in early-stage cancers or alongside other treatments.
Chemotherapy
- Drug-based treatment that targets cancer cells throughout the body.
- Typically used for advanced or aggressive cancers.
Immunotherapy
- Helps the immune system fight cancer more effectively.
Targeted Therapy
- Uses medications to block cancer cell growth without affecting normal cells.
Early-stage cancers often require less aggressive treatment, which is why early diagnosis is key.
Can Head and Neck Cancer Be Prevented?
While not all cases are preventable, you can significantly reduce your risk by following these steps:
- Quit Smoking and Avoid Tobacco Products
- Limit Alcohol Consumption
- Get the HPV Vaccine to prevent HPV-related cancers
- Wear Sunscreen on the face, neck, and lips
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene and schedule regular dental checkups
- Eat a Nutrient-Rich Diet with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Use Protective Equipment if working with hazardous chemicals
Early detection plays a huge role in successful treatment. If you notice persistent throat pain, voice changes, or lumps in your neck, schedule an evaluation with an ENT specialist.
When to See an ENT Specialist for Cancer Screening
You should consult an ENT doctor if you experience:
- A lump in the neck or throat that lasts more than 2 weeks
- Persistent voice changes or hoarseness
- Difficulty swallowing or pain when eating
- Chronic ear pain, especially in one ear
- Unexplained weight loss or chronic fatigue
An ENT specialist can conduct thorough screenings and, if necessary, refer you to an oncologist for further testing and treatment.